1. What is project risk management? Why is risk management necessary when managing projects?
So what is the project risk management process ? Every item or project can generate unexpected events. This event can be errors, bad impacts directly affecting the project or it can also be opportunities, good impacts, bringing benefits to the project. Project risk management is the process of assessing, identifying and researching problems that arise, and then making detailed plans to solve them.
The goal of project risk management is to increase the rate of positive impacts and reduce the rate of negative impacts on the project. Such event or condition should be identified and planned to deal with prevention right from the start of the project. The project manager and team need to observe the situation, assess what has happened and has not happened to eliminate potential hazards and seize potential opportunities.
 The project risk management process helps businesses deal with many problems
The project risk management process helps businesses deal with many problemsSo what are those common risks specifically? Just below are some examples of project risks businesses have been and will face when conducting a project:
- Over-optimistic in the process of budgeting and estimating completion time
- Budget cuts without prior notice
- Raw materials and manpower are not guaranteed
- Lack of interaction and exchange between stakeholders leads to disagreement
- The customer is not sure about the requirements for the project, causing the progress and goals of the project to constantly change
- The roles and responsibilities of each individual and department involved in the project are ambiguous
- Enterprises do not clearly understand the requirements of partners,...
Thus, we can see that project risk management is extremely important to every business. Good risk management for the project will bring many benefits to businesses
- Events can be either good or bad. Therefore, anticipating the arising situations will help the project team to proactively find the right measures to bring the best results.
- Project risk management planning helps businesses handle professionally, saving resources, time and costs.
- The project will be more practical and applicable if the risk management process is applied to all elements and elements of the project.
- Limiting adverse impacts on the project implementation process
- Strengthen management to help businesses operate smoothly and sustainably and increase brand value, finance, and market share in the business market.
2. Common risks in project management
A risk is any event that may occur that affects the performance, schedule and outcome of the project during the process. So, for project risk management to go smoothly, you need to identify common types of risks. The following are common business risks:
2.1 Positive risk and negative risk
Not all risks are created equal and have the same impact. Risk is often seen as a later consequence and has a positive or negative effect. Positive cases are seen as opportunities that businesses can seize to develop. In contrast, negative risks are damages that may affect the progress or outcome of the project.
 Positive and negative risks are easily recognized and are very common
Positive and negative risks are easily recognized and are very commonNegative risks are often foreseen and included in the project risk management plan to reduce adverse impacts. However, positive risks also require a smart approach to get the most out of the benefits avoiding those risks turning negative. Some positive risks in the projects of enterprises:
- Complete the project ahead of time
- Attract more engagement and interest from customers than expected
- Wider marketing opportunities thanks to carrier delays
- Monopolize the market for a period of time thanks to an earlier product launch
2.2 Risks by origin
Recognizing common risks helps businesses promptly reflect during the project. Besides the above two categories, risks are also classified by origin. Here are some common types that often appear in the field:
- External risk: This is the type of risk related to issues such as: law, regulation, environment, government; project location...
- Internal risks: Usually caused by issues such as: changes in policy by stakeholders, budgets, management team members and resource problems, etc.
- Technical risks: Due to changes in technology,...
- Commercial risk: This is the consequence of problems related to customers, partners, due to changes in contract terms,...
- Unforeseen risks: accounted for about 10%, often occur unexpectedly by management not foreseen.
 This type of risk mostly comes from external influences
This type of risk mostly comes from external influences2.3 Risk by outcome
Outcome risk is one of the types of events that often have negative consequences for a business. This group can be classified as follows:
- Enterprise risk: The risk of financial impact (profit or loss) of the project.
- Pure risk (Can be solved by insurance): Usually only the risk of loss such as work accident, theft, ...
2.4 Non-event risk
Most risks are predicted events that may or may not happen in the near future. However, there is another type of risk known as non-event risk, which includes the following types:
- Variability risk: This is the inability to predict what changes will occur in the future. For example, product sales may be higher or lower than the target, the number of defective products is more than expected during the inspection, etc. Risk of fluctuations, easy diversion affecting the project.
- Risk of ambiguity: Occurs due to lack of understanding, unclear about one or more issues. For example, unclear policies and requirements lead to the test product not matching the customer's required sample; do not fully understand the complexity of the project,... However, this type can be solved in many ways such as: exchanging ideas with a simulation product development expert,.....
 Non-event risks are unclear and unpredictable
Non-event risks are unclear and unpredictable3. The 6-step process of project risk management
How to deal with all the risks listed above effectively? The next section will share 6 project risk management steps to help readers' projects succeed.
3.1 Step 1: Identify risks
We will not be able to solve the problem without knowing what the risk is. Meet with the project management team and stakeholders, find individuals who have experience with the problem. Then, gather the information needed to identify and address the risk. Pay attention to possible problems, thoroughly study previously stored data to find all potential problems.
Once you've made sure you've listed all of the issues, dive deep into how the risk will impact the project. Try to minimize the risk as much as possible, evaluating the numbers in multiple dimensions. Use analytics to eliminate risks not risks.
3.2 Step 2: Risk analysis
Once the problem is identified, conduct an analysis and proactively resolve the problem that may occur. Using project management software will make it easier for managers to monitor projects. Through analysis and qualitative, you can determine how risk affects project outcomes, performance, and budget.
 How might this impact affect the project?
How might this impact affect the project?3.3 Step 3: Determine the treatment priority of the risks
The project management team should classify risks according to high, medium or low impact. As a result, a to-do list will be clearer and more seamless. Based on that, a series of plans will be detailed, preventable and can be addressed as soon as the risk starts to occur. Log an issue to track it down and get facts and a more effective solution next time.
Some risks often appear unexpectedly, unforeseeable, requiring businesses to pay more attention. These are the risks that have a high probability of derailing the project, the level of impact is almost the highest. Some risks are not too large, have little impact on progress, performance and budget usually do not have too big impact, can be noted for later treatment.
3.4 Step 4: Allocate responsibility for handling risks
Each project has its own importance, affecting the reputation of the company. An individual or an organization responsible for the work is essential. In fact, this is the step that needs to be addressed after identifying the risks and how to deal with them. Who is responsible, and how should it be determined and coordinated?
 The person in charge will manage and grasp the main situation
The person in charge will manage and grasp the main situationDelegating tasks to the right people is better for the project because they are experienced, willing to take risks and have the ability to lead the team. Identifying risks is one thing, but if no one is in charge, the project is very unlikely to succeed. Addressing whenever problems arise, without a plan to deal with the consequences, the project team is putting the company at more risk.
3.5 Step 5: Determine action on risk
Here are some ways to determine the right action plan to respond to risks:
| Strategy | Apply for | Purpose | Act |
| Avoid (Not Likely) ) |
Hazards/risks affecting the overall project |
Avoidance is a strategy to help eliminate threats, protect the project. The planning team may change some of the original project elements or goals to reduce the likelihood of impact to zero. |
- Resolve the cause of the risk - Prolong project progress - Change strategy - Narrow the scope - Collecting information and clarifying customer needs - Enhance professional knowledge |
| Mining (It's Sure to Happen) |
Hazards/risks affecting the overall project High priority |
This strategy is often chosen to apply with risks that bring opportunities to the project. The organization or business will seek to seize the opportunity to ensure that the event 100% happens. |
- Use new technology or technological innovation to reduce costs and save time. - Having the help of many talents outside the project helps speed up progress. |
| Mitigation |
Hazards/risks affecting the overall project, high priority |
- This is the strategy implemented to minimize the negative impact on the project. Mitigating action is often more effective than trying to fix the consequences. - In cases where it is not possible to mitigate the occurrence/occurrence of the risk, this strategy can reduce the impact on the campaign. |
- Adopt a simpler production process - Conduct more tests - Choose a more reliable contractor - Producing backup models for important, high-complexity projects |
| Advanced |
Opportunities/risks affecting the overall project |
This strategy is often used by businesses to increase the likelihood - the impact of a risk. The likelihood of an opportunity can be increased by focusing on the cause. It's more beneficial to try to strengthen early than to reap the benefits later. If it's not possible to increase the likelihood, the team may consider redirecting the focus to factors that can increase the utility of the project. |
- Use a lot of manpower to shorten the operation time - Attract many contractors to increase the project rate |
| Transfer |
Hazards/risks affecting the overall project, low priority |
- If a threat occurs, handover is the preferred strategy for transferring impact to a third party. - Allocation of risks including payment of loss costs to the acceptor. |
- Using insurance, contract regulations,... Some agreements between two parties may transfer responsibility to other parties. |
| Share |
Opportunities/risks affecting the overall project; low priority |
As opposed to transfer, this is a strategy of sharing with a third party even if it is a benefit or/and impact. An important element of this strategy lies in the need for businesses to find a reliable partner and be able to seize opportunities for mutual purposes. |
Forming partnerships and joint ventures to share opportunities. |
| Climb the ladder |
Danger/opportunity, low priority |
This strategy is applied in cases where the project is judged to be outside the scope of the project by the sponsor or the project team. At this point, the response options are no longer appropriate and outside the project management's authority. The risk presented will be managed at the portfolio or program level under the management of the organization. |
The threats/opportunities presented are often aligned with the target to be affected. Although reported, these threats/opportunities will not be further monitored. |
| Accept |
Opportunities/risks/threats affecting the overall project, low priority |
Acceptance is a strategy applied to threats/opportunities that are not too serious or that there are no effective measures that can be used to suppress/exploit. The project team did not take a specific action on the event. |
Establish a contingency that includes a plan, budget, time, or resources to deal with or take advantage of an opportunity. Passive acceptance does not include proactive actions other than periodic monitoring to avoid major changes. |
3.6 Step 6: Continuous risk monitoring and assessment
An indispensable step in the project risk management process is risk monitoring and assessment. This is the process of monitoring the implementation of identified risk response plans; Analyze new project management risks and evaluate process effectiveness. Risk monitoring and assessment allows us to inform the next steps of the project on aggregate and individual risk information and data.
To ensure that the current level of risk is recognized in a timely and correct manner, this process needs to take place continuously and throughout the project. The monitoring process will track new risks, changing risks, and the overall positive/negative level of the project. Some of the following questions will help make the monitoring process clearer:
- Have the remedial measures been planned effectively?
- How is the overall level of risk changing?
- Has the status of low priority risks changed?
- What is the emerging risk? How to solve?
- Are the project's assumptions still relevant?
- How are risk management policies and procedures followed?
- Has the change of provisions been resolved?
- Is the risk management strategy effective?
4. Effective risk management solutions
To manage project risks effectively and intelligently, learning some supporting tools is a fundamental step. The next part will be Viindoo's reveal to customers some forms and tools to help solve project risk management.
4.1 Sample excel file for project risk assessment and management
Here are some sample project risk management Excel files . Consult now!
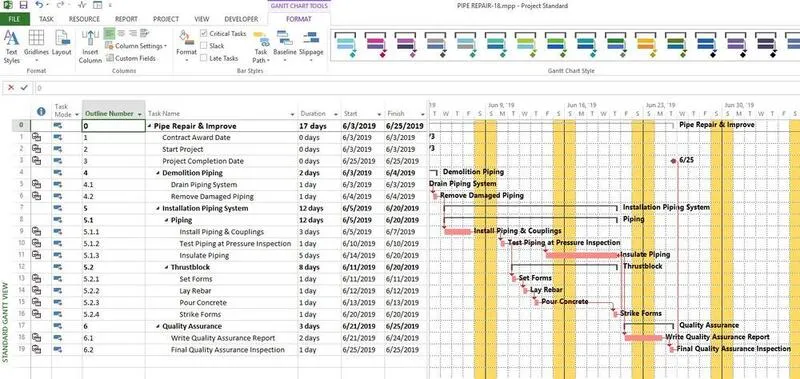 Manage a variety of information in many categories
Manage a variety of information in many categories4.2 Using Gantt charts
Gantt chart is always the top priority of businesses in managing and presenting problems. Full job scheduling, assignment and monitoring tools. This type of chart also allows team members to add comments and edit information as needed. At the same time, each individual can keep track of his or her tasks to complete on time. Managers can see the article A few examples of Gantt diagrams for beginners to better understand this chart.
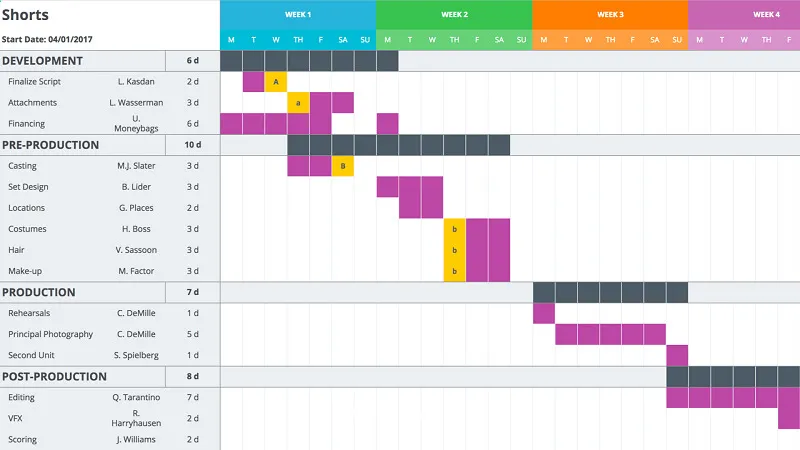 Gantt chart helps managers keep track of project progress
Gantt chart helps managers keep track of project progress4.3 Using Kanban
What is Kanban ? Kanban boards help project teams align and prioritize urgent, high-impact risks. The tool allows customization to identify tasks that could be risky for the project. Besides, the software not only supports project risk management but also project management. Readers can completely use the software only to manage risks and assess the speed of group processing.
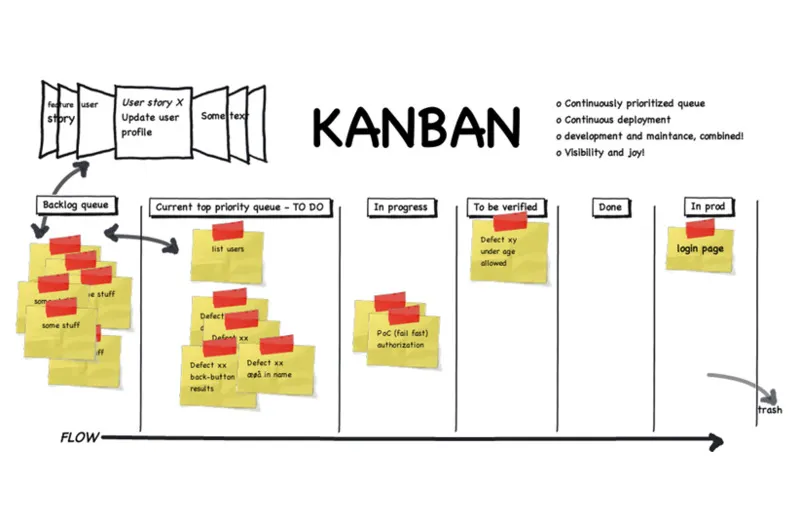 Model of using Kanban board in the project
Model of using Kanban board in the projectProject risk management is complex and multi-step. Without a suitable project management software or any supporting tools, this will be a difficult job for many employees. Contact Vietnam Manpower immediately if readers are looking for solutions to help optimize possible risks, save resources and reduce pressure on everyone.












Replies to This Discussion