What is additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding successive layers of material until a final shape is achieved. It's a digital fabrication process that allows for the creation of complex geometries and custom designs.
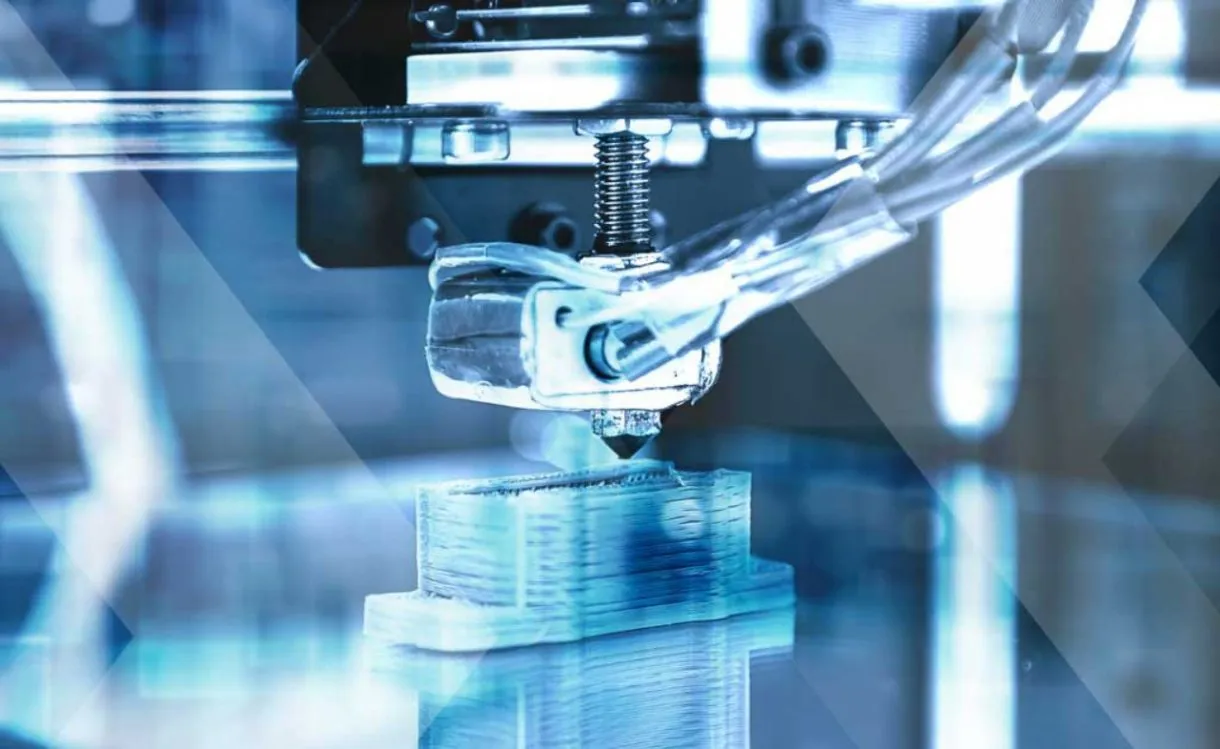

What is additive manufacturing?
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve subtractive manufacturing, additive manufacturing builds products in layers.
Types of additive manufacturing
There are several types of additive manufacturing technology, each with its own strengths and limitations. Some of the most common types of 3D printing include:
Fused deposition model (FDM)
FDM is the most widely used 3D printing technology. In this process, a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle, creating a layer of material that solidifies as it cools. The process is repeated layer by layer until the final product is reached.
Embossing Technology (SLA)
SLA uses a laser to solidify liquid plastic, creating a solid layer. The process is repeated layer by layer until the final product is reached. SLAs are often used for highly detailed and precise parts, such as dental and medical models.
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
SLS uses a laser to selectively fuse powder particles together, creating a solid layer. The process is repeated layer by layer until the final product is reached. SLS is often used for functional prototypes and end-use parts.

What is additive manufacturing - Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP is similar to SLA, but instead of using a laser, it uses a light source to solidify liquid plastic. DLP is often used for small, high-resolution parts.
Advantages of additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Some of the key advantages include:
Flexible design
Additive manufacturing allows the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This means that designers can create parts and products with more creative freedom, resulting in more innovative designs.
Cost-effective production
Additive manufacturing can be a cost-effective production method, especially for small manufacturing operations. This is because the cost of producing individual parts is relatively low and produces less waste than subtractive manufacturing methods.

Cost-effective production
Faster prototyping
Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping, which can significantly reduce product development time. Designers can quickly create and test multiple product iterations, allowing them to refine the design and identify any problems early in the development process.
Mass customization
Additive manufacturing allows for large-scale product customization. This means that companies can manufacture products tailored to each customer's needs without incurring the high costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Reduce environmental impact
Additive manufacturing can have a smaller environmental footprint than traditional manufacturing methods. This is because it generates less waste and the manufacturing process can be more energy efficient.
Applications of additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing has many applications in various industries. Some of the most popular applications include:
Aerospace and Defense
Additive manufacturing is used in the aerospace and defense industries to create light and complex parts, such as engine parts and aircraft wings. 3D printing allows engineers to design and manufacture parts with complex shapes that cannot be manufactured using traditional methods.
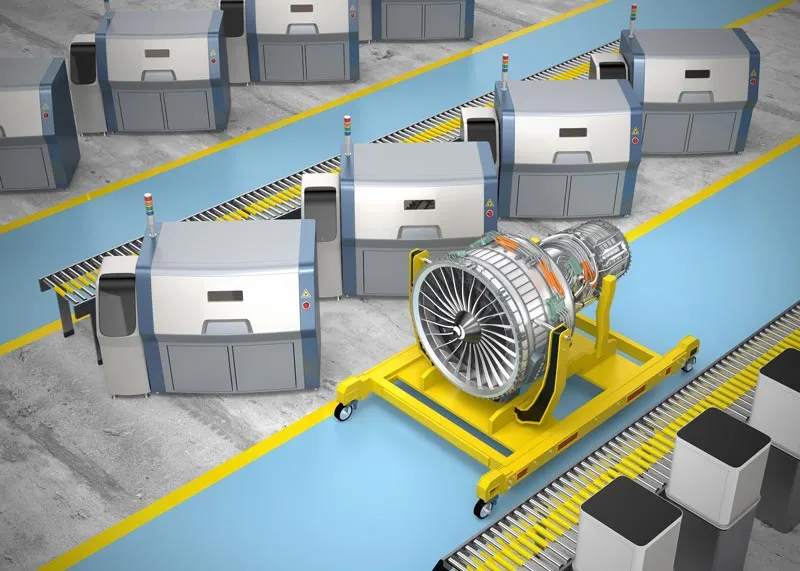
Aerospace and Defense
The technology also enables faster prototyping and allows for customization of parts, which can result in cost savings and improved performance.
Car
Additive manufacturing is used in the automotive industry to create prototypes, custom parts, and tooling. This technology can be used to manufacture complex parts and shapes with high precision.
This can be especially useful in creating parts for specialized or low-volume vehicles. 3D printing can also be used to create molds and fixtures, which can reduce the production time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Biomedical engineering
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized the field of biomedical engineering by enabling the creation of patient-specific medical devices, implants, and prostheses. This technology can be used to create complex geometries and structures, which can be customized to a patient's unique anatomy.
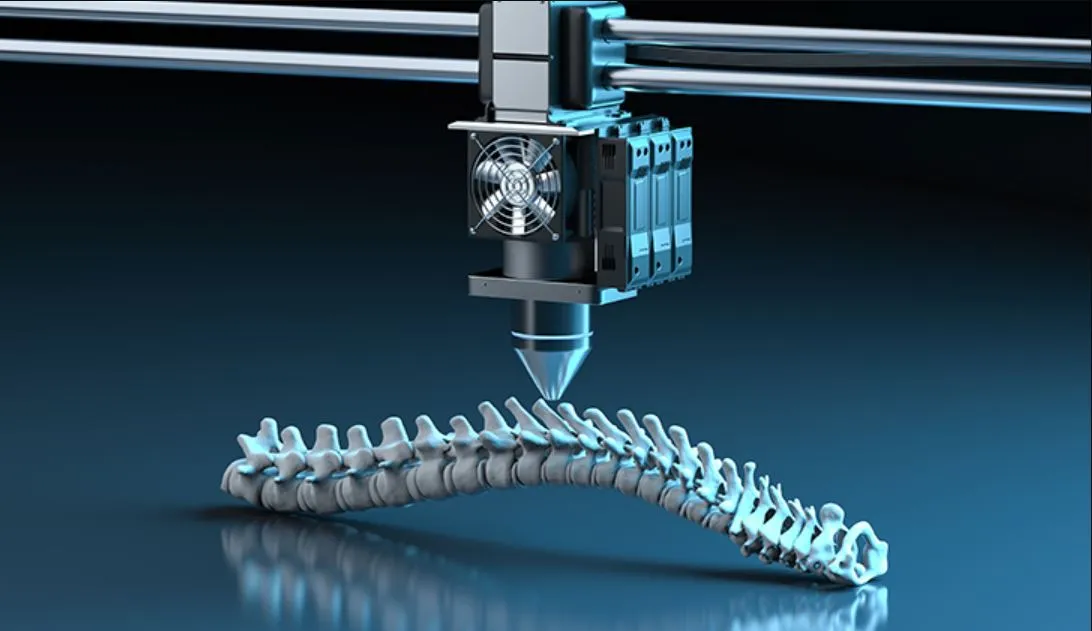
Biomedical engineering
3D printing can also be used to create surgical models and guides, helping doctors plan and practice surgical procedures.
>>>>> Read more: Discover Types of Additive Manufacturing Materials
Architecture and construction
Additive manufacturing is being used in the architecture and construction industry to create complex and custom building components, such as facades and columns.
Additive manufacturing can also create molds and formwork, which reduces the time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing can also be used to produce sustainable building materials, such as biodegradable plastics made from plant-based materials.
Jewelry and Fashion
Additive manufacturing can create custom designs and unique products in the jewelry and fashion industries.
This technology can be used to create intricate and detailed designs that are difficult or impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing can also be used to create molds and patterns for molding and crafting traditional jewelry and fashion items.
Education and Research
Additive manufacturing is being used in education and research to teach students about engineering and design principles, and to facilitate research into new materials and manufacturing processes.
This technology can be used to create physical models and prototypes for student designs and to create prototypes for research projects.
What is additive manufacturing ? One thing we know about additive manufacturing is that it has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by providing cost-effective manufacturing, design flexibility, and reduced environmental impact. With a wide range of applications, it is poised to continue to change the way products are made.












Replies to This Discussion