Data lifecycle in the enterprise
Enterprise data are structured units of information formed from the operations of an enterprise.
Data includes information about the issues and objects with which the business interacts, such as employees, customers, suppliers, sales orders, orders, production processes, etc.
These data will have attributes, such as name, address, date, etc. And the data also has certain relationships with each other that businesses can rely on to perform analysis.
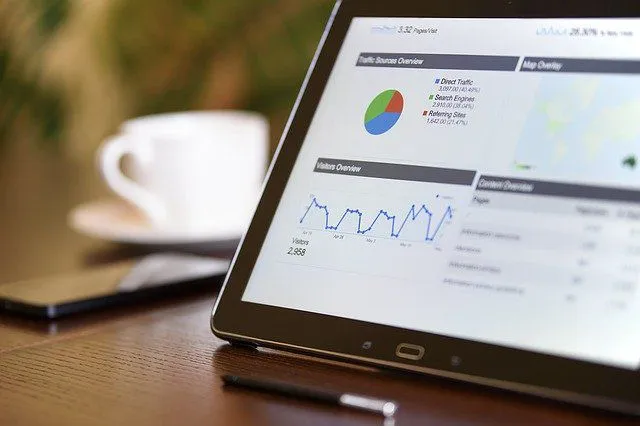

The importance of data in business
Data helps business leaders make decisions based on changes, trends, and statistics. For example:
HR Managers use data such as recruiting success rates and channel costs to gauge the effectiveness of channel recruiting.
Marketing Managers use customer data, quotes, and orders to categorize customers, analyze customer behavior, and analyze the effectiveness of campaigns.
Higher levels of management such as the CEO or the Board of Directors use data to see macro issues: fluctuations in input prices of goods and materials, transportation costs; Production efficiency; change in revenue, etc.
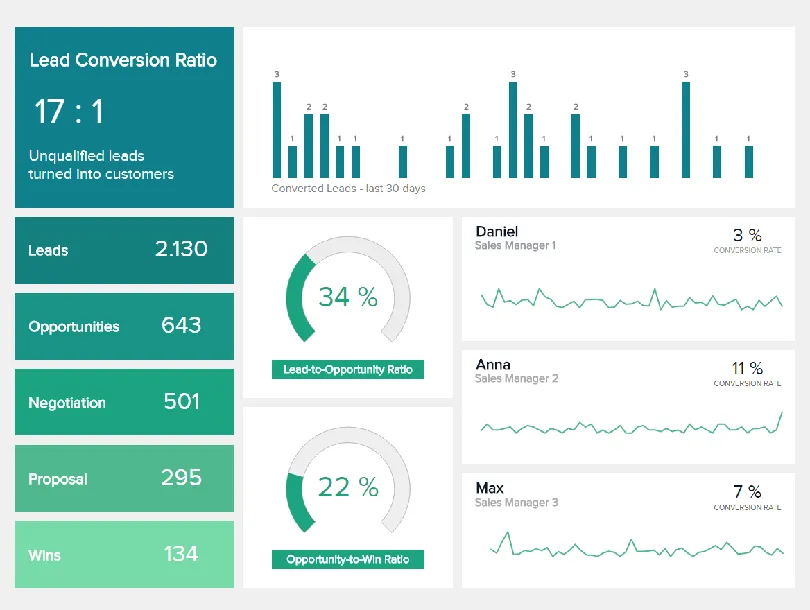
Businesses can optimize their operations and manufacturing processes by effectively using the power of the lifecycle of data to dramatically enhance the customer experience. From there, businesses can grow revenue strongly while ensuring cost optimization.
How was the data formed and used?
Most of the data that is formed in the enterprise goes through a multi-stage life cycle. According to the Wiley CMAexcel Learning System (WCMALS) - 2020 Edition, there are eight stages in the Data Life Cycle , as shown in the diagram below:
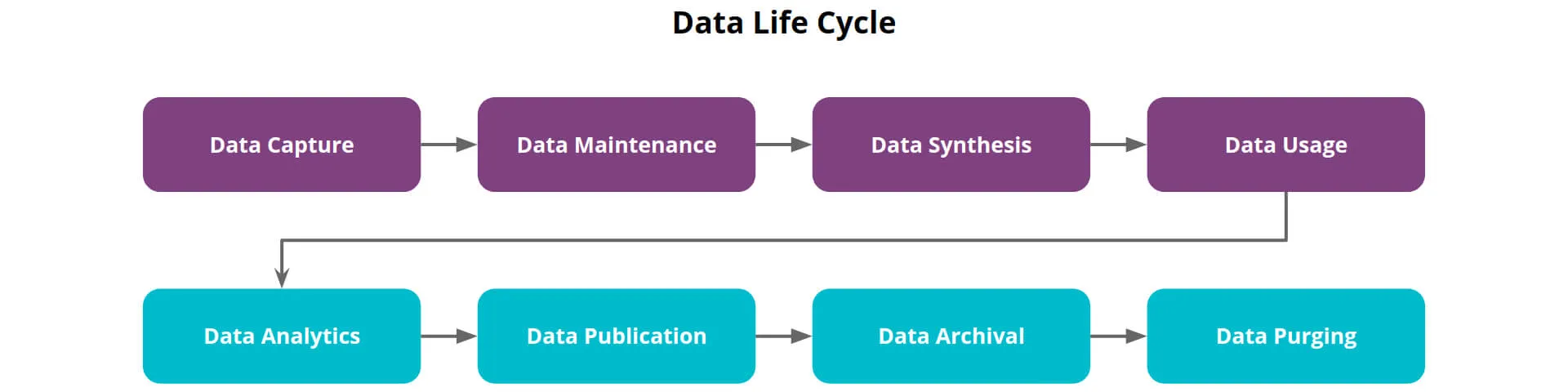
Enterprise data loop diagram
-
Data Collection System Tu: This is the first stage in the Data Life Cycle. Typically, data within an enterprise is collected through three forms:
-
Manual data entry: create data by manual input. We can think of using ERP software in the business, salespeople create Quotations, or accountants write Invoices on ERP software. A data item is created.
-
Data collection: import existing data generated from organizations outside the business. A typical example of Data Acquisition is the feature of automatic data integration through API of some modern ERP software with internet banking system to serve for reconciliation and accounting of payment transactions.
-
Signal reception: collects data from devices used in business operations. For example, in the access control process of company personnel, data is generated from employees performing fingerprint scanning for login and logout. The data is then integrated into the administrative software or extracted as Excel.
-
-
Data maintenance: Data needs to be transformed into a user-friendly form in order to be usable. This transition may include: migration, integration, cleaning, enrichment, changed data collection, etc.
-
Data aggregation: This phase of the data lifecycle includes statistical methods that combine data from multiple sources or experiments. This is to get better overall estimates and answers to data requests. A good example of Data Aggregation is the use of modeling methods to support investment decisions, such as risk modeling, financial modeling, and computational modeling.
-
Data usage: Data usage is how data is used to support business tasks, such as strategic planning, customer relationship management (CRM), invoice processing, order submission, and more. order to supplier, etc.
-
Data Analytics: During this phase of the data lifecycle, people use data analytics methods to turn raw data into useful information and business insights. A widely used method in business data analysis is data visualization
-
Data Disclosure: Data sent or disclosed outside the organization, such as sending quotes to customers, submitting debit comparisons, or publishing financial statements to a company website.
-
Data archiving: This process involves removing data from the usable environment, putting it in storage, and reusing it in the future.
-
Erase data : This is the last step of the data life cycle to delete unused or unnecessary data from the storage system. Data deletion should be planned and considered with legal requirements or the company's information protection policy.
For example, according to Decision 376/2003/QD-NHNN on the preservation and storage of electronic documents used for accounting and capital payment of payment service providers, the electronic certificates are directly related. to the accounting records at the payment service provider: must be kept for 20 (twenty) years from the end of the accounting year or when the payment service provider completes the settlement. capital.

Many businesses have their own data analysis teams or hire consulting firms - analytics
In short, understanding the lifecycle of data , controlling and effectively using it is the vital mission of a business. Viindoo hopes that after this article, you have gained the background knowledge about data that you can apply to your business.












Replies to This Discussion