Why is Positive Psychology Important?
By directing attention towards strengths, positive emotions, engagement, meaningful relationships, and accomplishments, positive psychology fosters a positive work environment. Leaders can leverage these principles to inspire and motivate teams, cultivating a culture of collaboration, resilience, and job satisfaction. This approach not only enhances individual work experiences but also contributes to the overall success and productivity of organizations.
The PERMA Model and Leadership
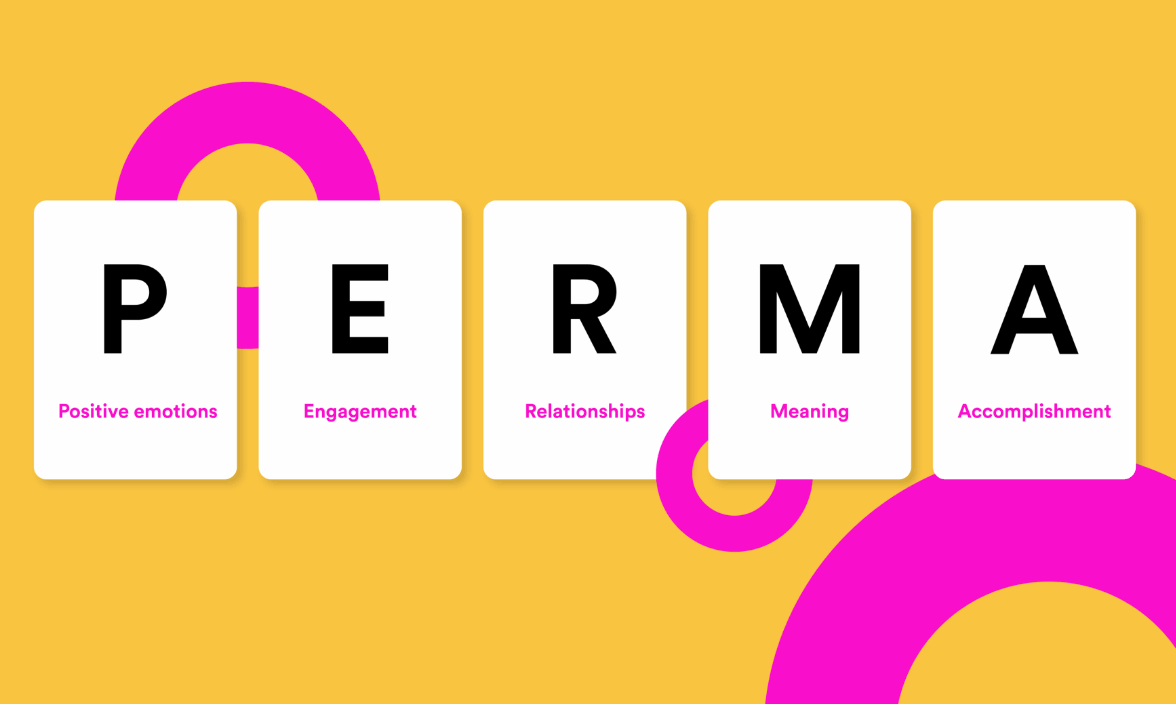
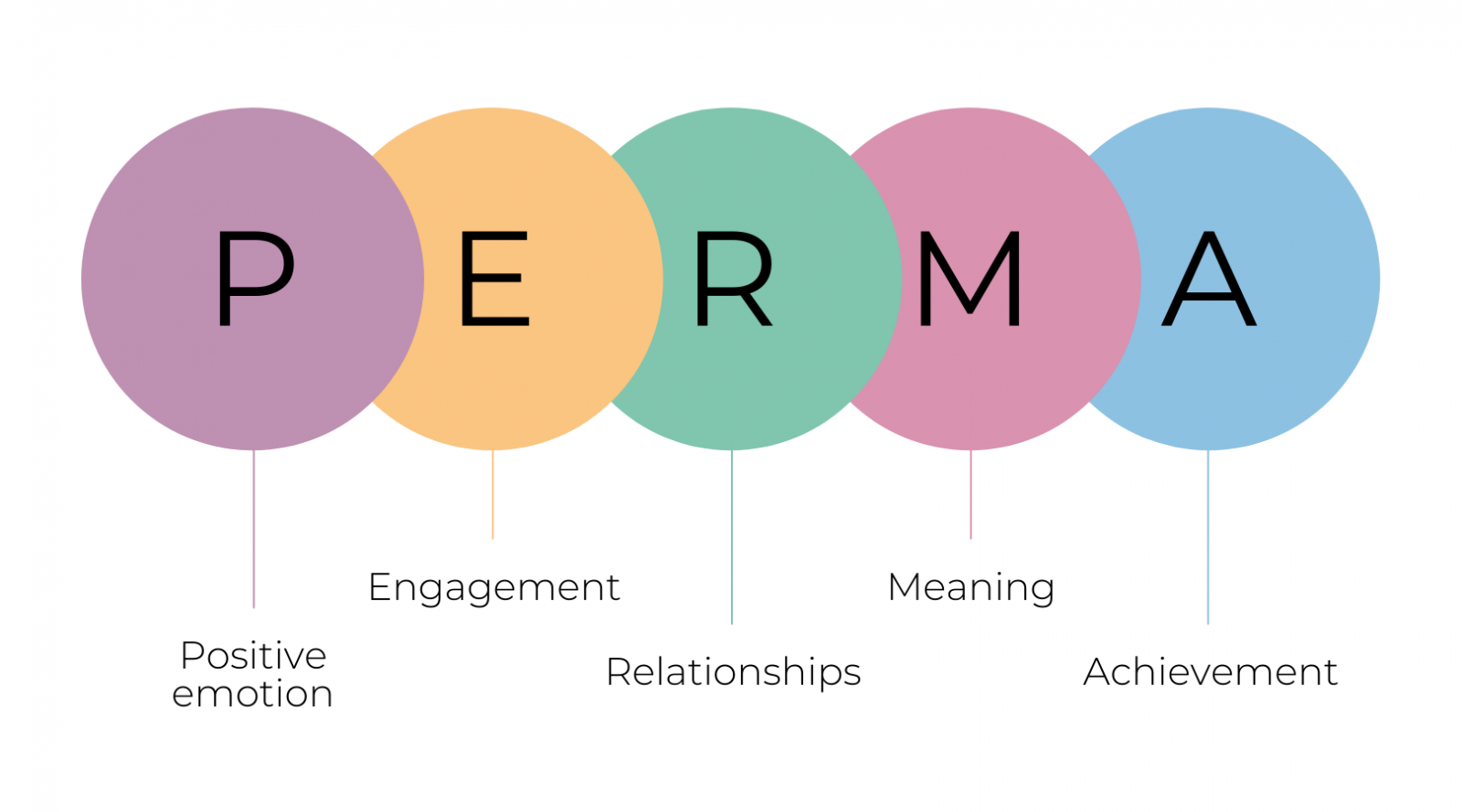
Martin Seligman’s PERMA model, introduced in 2011, outlines five essential elements for well-being: Positive Emotion, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment.
Positive Emotion (P)
Leaders should embrace positive emotions like hope, joy, and gratitude to create a vibrant work environment. Encouraging self-reflection and building a sense of belonging transforms mindsets, fostering trust and collaboration. Leaders play a key role in influencing a positive atmosphere, addressing negativity, and reducing stressors.
Shawn Achor, a leading positive psychology researcher, gained widespread recognition for his TED Talk, “The Happy Secret to Better Work.” In the talk, Achor challenges the notion that success precedes happiness, advocating for the reverse. He introduces the “happiness advantage,” asserting that a positive mindset leads to increased success. Achor blends humor with scientific insights, offering practical strategies to cultivate happiness, such as gratitude practices and acts of kindness. His engaging presentation has resonated globally, contributing to the popularization of positive psychology concepts and highlighting the transformative power of happiness on personal and professional achievement.
Engagement (E)
Enhancing engagement involves aligning individual strengths with organizational needs, unlocking improved performance and positive behaviors. Leaders can promote autonomy, encourage flow experiences, and establish programs for meaningful relationships and mentorship.
The concept of flow experience, introduced by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, refers to a state of optimal engagement and focus in which individuals become fully immersed in a challenging task. This immersive state occurs when the level of skill matches the level of challenge, resulting in a harmonious and highly satisfying experience. Achieving a flow state often leads to increased creativity, heightened productivity, and a deep sense of fulfillment. Employees who regularly experience flow are more likely to find joy and meaning in their work, contributing to a positive and thriving workplace culture. Cultivating environments that encourage such optimal experiences can enhance job satisfaction and overall well-being among employees.
Relationships (R)
Building positive relationships is vital for team success. Leaders should support programs that cultivate meaningful connections, mentorship, and learning communities, promoting collaboration and mutual support.
Meaning (M)
Meaning is illuminated when individuals align personal purpose with organizational objectives. Leaders can communicate task significance clearly, engage in dialogues to understand employee roles, and encourage the infusion of personal values into work.
Accomplishments (A)
Leaders should cultivate a culture of innovation, autonomy, and aligned incentives, openly recognizing achievements and celebrating milestones. This approach fosters a positive, supportive environment.
What you need to know about Positive Psychology
- Positive psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the positive aspects of human experience, well-being, and personal strengths.
- It emerged as a response to traditional psychology’s predominant focus on mental illnesses and dysfunction.
- Martin Seligman, often considered the founder of positive psychology, introduced the PERMA model, highlighting five essential elements for well-being: Positive Emotion, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment.
- Positive psychology aims to enhance individuals’ overall life satisfaction, happiness, and fulfillment.
- It emphasizes the cultivation of positive emotions, strengths, resilience, optimism, and a sense of meaning in life.
- Applications of positive psychology extend to various domains, including education, workplace settings, mental health, and personal development.
- Positive psychology interventions include exercises and practices designed to improve well-being, such as gratitude journals, mindfulness, and character strengths assessments.
- The field recognizes the importance of fostering positive relationships, social connections, and a sense of community for overall happiness.
- Well-being is viewed as a multifaceted concept, encompassing emotional, social, and psychological dimensions.
- Positive psychology complements traditional psychology by providing a more comprehensive understanding of human flourishing and optimal functioning.












Replies to This Discussion