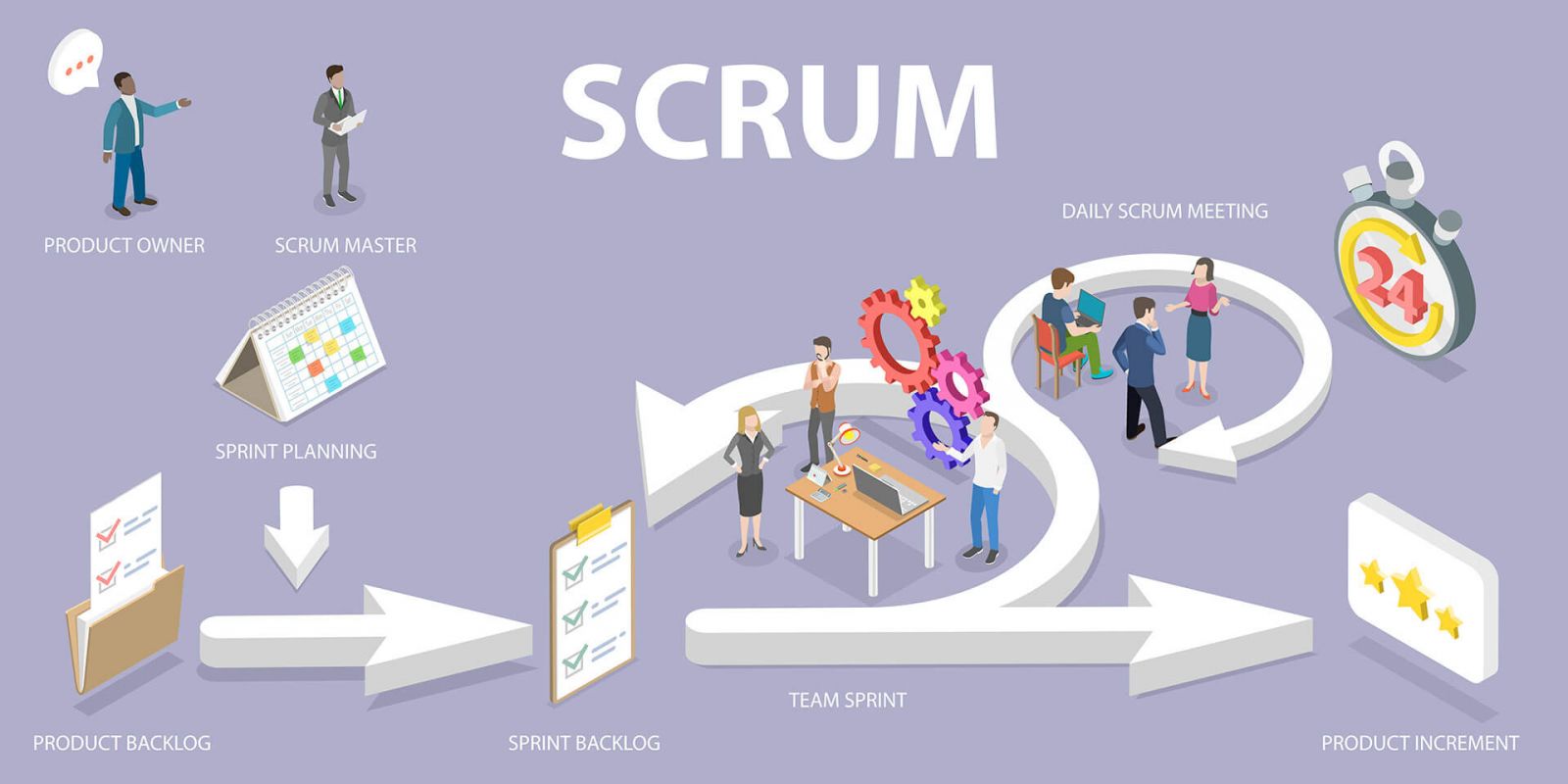
What are Scrum artifacts?
Scrum artifacts are tangible byproducts of the Scrum process that provide information about project progress and keep the team on track. They serve as a means of communication and collaboration between the team, stakeholders, and customers. According to the Scrum Guide, there are three main components in Scrum: Product Backlogs, sprint backlogs, and Increments.
Product Backlogs
The Product Backlog is a prioritized list of all the features, requirements, and improvements that need to be implemented in a project. It is the Product Owner's responsibility to maintain and continuously improve the Product Backlog, ensuring that it reflects the project's current priorities and needs. The Product Backlog is dynamic and evolves throughout the project, with new items added or removed based on feedback and change requests.
Purpose of Product Backlog
The Product Backlog serves as the single source of truth for project scope and requirements. It provides transparency for, allowing the team to understand what needs to be done and why. By having a clear and prioritized list of items, the team can focus on delivering the most valuable features first, ensuring that project goals are met.

How to use Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is continuously refined and updated throughout the project. The product owner works closely with the team to ensure that items in the backlog are clearly identified, estimated, and prioritized. The team will then select a set of items from the Product Backlog to work on in the upcoming Sprint, based on their capacity and the priority set by the Product Owner.
Product Backlog example
| Item | Prioritize | Estimated effort |
|---|---|---|
| User registration feature | High | 5 story points |
| Payment integration | Medium | 8 story points |
| Email notification system | Short | 3 story points |
Sprint Backlogs
The Sprint Backlog is a subset of the Product Backlog, containing the items the team has committed to completing in the current Sprint. It is created during the Sprint Planning meeting and is owned by the Development Team. The Sprint Backlog is a living document that is continuously updated as the team progresses through the Sprint.
The purpose of the Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog provides transparency about the work the team has committed to completing during the Sprint. It keeps the team focused and on track, ensuring that they are working towards achieving the Sprint goal. By having a clear understanding of what needs to be done, the team can make informed decisions and adjust as needed to deliver a deliverable product increment at the end of the Sprint.
How to use the Sprint Backlog
During the Sprint Planning meeting, the team selects items from the Product Backlog that they will commit to completing during the Sprint. They then divided these items into smaller tasks and estimated the effort required for each task. The Sprint Backlog is then used as a guide throughout the Sprint, with the team updating it as they complete tasks and encounter new information or obstacles.
Sprint Backlog example
| Item | Mission | Assigned | Estimated effort |
|---|---|---|---|
| User registration feature | User interface design | John | 3 o'clock |
| User registration feature | Develop auxiliary functions | Sarah | 5 hours |
| Payment integration | Research payment providers | Tick | 2 o'clock |
| Email notification system | Implement email templates | Emily | 4 hours |
Growth section
The Increment is the sum of all completed Product Backlog items at the end of the Sprint. It is the tangible result of the team's work and must be usable and deliverable. Increments are tested during the Sprint Review meeting and can be released to customers or stakeholders if deemed ready.
Purpose of the Growth Section
Increments provide transparency into the progress the team has made during the Sprint. It enables value to be delivered early and often to customers and stakeholders, allowing them to provide feedback and make any necessary changes. By increasing the working product at the end of each Sprint, the team can continuously adjust and improve its work based on feedback.
How to use Growth Part
Increments are tested during the Sprint Review meeting, where the team presents completed items to stakeholders and gathers feedback. Based on this feedback, the team can make adjustments and improvements to the product version before releasing it to customers or stakeholders. Increments also serve as the basis for future Sprints, with new features and enhancements built upon.












Replies to This Discussion